NSF 20-570: Industry-University Cooperative Research Centers Program (IUCRC)
Program Solicitation
Program Solicitation NSF 20-570
|
National Science Foundation |
Preliminary Proposal Due Date(s) (required) (due by 5 p.m. submitting organization’s local time):
July 07, 2020
September 16, 2020
March 10, 2021
Second Wednesday in March, Annually Thereafter
September 08, 2021
Second Wednesday in September, Annually Thereafter
Preliminary proposals are required prior to submission of planning grants. Submitters seeking a waiver of the planning grant stage must submit the waiver request as a preliminary proposal.
Full Proposal Target Date(s):
September 08, 2020
December 16, 2020
June 09, 2021
Second Wednesday in June, Annually Thereafter
December 08, 2021
Second Wednesday in December, Annually Thereafter
Important Information And Revision Notes
- Preliminary Proposals are required only for Planning Grants and Planning Grant waivers.
- A Planning Grant has a duration of up to 12 months and the award size has been increased from $15,000 to $20,000. Please note that the Planning Grant proposals described in this solicitation are a solicitation-specific project category and are separate and distinct from the Planning type of proposal described in Chapter II.E.1 of the PAPPG. When preparing a Planning Grant proposal in response to this solicitation, the “Research” type of proposal should be selected.
- IUCRCs funded under this solicitation are eligible to apply for two five-year Phases of funding. Active Phase II Centers funded under prior solicitations have the option of competing for a Phase III award. The new Phase II funding model will consist of two designations based on membership participation and funding levels: Phase II and Phase II-Plus (denoted II+). Phase II+ provides a higher level of NSF support with a proportionately higher level of industry membership.
- Multi-site Centers will consist of a Lead Site and Partner Sites, requiring centralized coordination, management, and operations by the Lead Site.
- For multi-site Centers, a financial plan and a Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) between all Sites is required for how Center operations are funded at the Lead Site.
- There are two levels of Center membership allowed under this solicitation – Full Members and Associate Members.
- Companies of all sizes/types (large and small businesses, startups, for-profit and non-profit entities) are encouraged to participate as Members, as are government agencies (federal, state and local).
- For NSF Directorates with topic-specific portfolios (i.e., Geosciences (GEO); Social, Behavioral, and Economic Sciences (SBE)), IUCRCs will be considered only on topics of interest distributed via Dear Colleague Letters. Please check the NSF website or call the cognizant Program Director in GEO or SBE.
Any proposal submitted in response to this solicitation should be submitted in accordance with the NSF Proposal & Award Policies & Procedures Guide (PAPPG) that is in effect for the relevant due date to which the proposal is being submitted. The NSF PAPPG is regularly revised and it is the responsibility of the proposer to ensure that the proposal meets the requirements specified in this solicitation and the applicable version of the PAPPG. Submitting a proposal prior to a specified deadline does not negate this requirement.
Summary Of Program Requirements
General Information
Program Title:
Industry-University Cooperative Research Centers Program (IUCRC)
Synopsis of Program:
Program Mission:
The IUCRC program catalyzes breakthrough pre-competitive research by enabling close and sustained engagement between industry innovators, world-class academic teams, and government agencies. IUCRCs help industry partners and government agencies connect directly and efficiently with university researchers to achieve three primary objectives: 1) Conduct high-impact research to meet shared and critical industrial needs in companies of all sizes; 2) Enhance U.S. global leadership in driving innovative technology development, and 3) Identify, mentor and develop a diverse, highly skilled science and engineering workforce.
Program Overview:
The IUCRC program provides a structure for academic researchers to conduct fundamental, pre-competitive research of shared interest to industry and government organizations. These organizations pay membership fees to a consortium so that they can collectively envision and fund research, with at least 90% of Member funds allocated to the direct costs of these shared research projects.
IUCRCs are formed around research areas of strategic interest to U.S. industry. Industry is defined very broadly to include companies (large and small), startups and non-profit organizations. Principal Investigators form a Center around emerging research topics of current research interest, in a pre-competitive space but with clear pathways to applied research and commercial development. Industry partners join at inception, as an existing Center grows or they inspire the creation of a new Center by recruiting university partners to leverage NSF support. Government agencies participate in IUCRCs as Members or by partnering directly with NSF at the strategic level.
Universities, academic researchers, and students benefit from IUCRC participation through the research funding, the establishment and growth of industry partnerships, and educational and career placement opportunities for students. Industry Members benefit by accessing knowledge, facilities, equipment, and intellectual property in a highly cost-efficient model; leveraging Center research outcomes in their future proprietary projects; interacting in an informal, collaborative way with other private sector and government entities with shared interests; and identifying and recruiting talent. NSF provides funding to support Center administrative costs and a governance framework to manage membership, operations, and evaluation.
Successful IUCRCs require:
- A capable research/management team with an entrepreneurial mindset;
- Universities, faculty, and students interested in engaging in research of interest to industry;
- A community of industry partners seeking pre-competitive, use-inspired research projects.
Each IUCRC is expected to grow and become independently sustainable by the end of the NSF support.
Cognizant Program Officer(s):
Please note that the following information is current at the time of publishing. See program website for any updates to the points of contact.
-
Prakash G. Balan, IUCRC Lead Program Director, Directorate for Engineering, telephone: (703) 292-5341, email: pbalan@nsf.gov
Seetha Raghavan, IUCRC Program Director, telephone: (703) 292-4580, email: seraghav@nsf.gov
-
Mohan Kumar, IUCRC Program Director, Directorate for Computer & Information Science & Engineering, telephone: (703) 292-7408, email: mokumar@nsf.gov
-
Ann C. Von Lehmen, IUCRC Program Director, Directorate for Computer & Information Science & Engineering, telephone: (703) 292-4756, email: avonlehm@nsf.gov
-
Barbara L. Ransom, IUCRC Program Director, Directorate for Geosciences, telephone: (703) 292-7792, email: bransom@nsf.gov
-
Rebecca Ferrell, IUCRC Program Director, Directorate for Social, Behavioral & Economic Sciences, telephone: (703) 292-7850, email: rferrell@nsf.gov
Jeffrey M. Stanton, IUCRC Program Director, telephone: (703) 292-7794, email: jstanton@nsf.gov
Thomas S. Woodson, IUCRC Program Director, telephone: (703) 292-5150, email: tswoodso@nsf.gov
-
José R. Almirall, IUCRC Program Director, Directorate for Mathematical and Physical Sciences, telephone: (703) 292-7434, email: jalmiral@nsf.gov
Applicable Catalog of Federal Domestic Assistance (CFDA) Number(s):
- 47.041 --- Engineering
- 47.049 --- Mathematical and Physical Sciences
- 47.050 --- Geosciences
- 47.070 --- Computer and Information Science and Engineering
- 47.074 --- Biological Sciences
- 47.075 --- Social Behavioral and Economic Sciences
- 47.076 --- STEM Education
- 47.079 --- Office of International Science and Engineering
- 47.083 --- Office of Integrative Activities (OIA)
- 47.084 --- NSF Technology, Innovation and Partnerships
Award Information
Anticipated Type of Award: Standard Grant or Continuing Grant
Estimated Number of Awards: 10
2 to 8 full Center awards and 4 to 6 Planning Grant awards annually.
Anticipated Funding Amount: $20,500,000
Individual award sizes (total costs):
$20,000 for Planning Grants
$150,000 per year for Phase I
$100,000 per year for Phase II
$150,000 per year for Phase II+
$50,000 per year for Phase III
Planning Grants are intended to be awarded as standard grants. All Center Site Grants will be awarded as Continuing Grants.
Estimated program budget, number of awards and average award size/duration are subject to the availability of funds.
Eligibility Information
Who May Submit Proposals:
Proposals may only be submitted by the following:
- Institutions of Higher Education (IHEs) - Two- and four-year IHEs (including community colleges) accredited in, and having a campus located in the US, acting on behalf of their faculty members. Special Instructions for International Branch Campuses of US IHEs: If the proposal includes funding to be provided to an international branch campus of a US institution of higher education (including through use of subawards and consultant arrangements), the proposer must explain the benefit(s) to the project of performance at the international branch campus, and justify why the project activities cannot be performed at the US campus.
Who May Serve as PI:
The Principal Investigator (PI) on a proposal must be a tenured faculty member. Requests for waivers to allow non-tenured faculty or research staff to serve as PI must be submitted in writing to the cognizant Program Officer by the PI's supervisor (e.g., Department Chair or Dean) in advance of proposal submission. Further, written approval from the cognizant Program Director is required prior to proposal submission and should be included as a Single Copy Document in the proposal. The PI must act as the initial Site Director. A PI/Co-PI can have only one active IUCRC Site award at any given time.
Limit on Number of Proposals per Organization:
There is no limit to the number of proposals an eligible organization may submit to this program as long as each proposal pertains to a different IUCRC.
Limit on Number of Proposals per PI or co-PI:
PIs and Co-PIs can only submit one proposal per submission period. A PI/Co-PI can have only one active IUCRC Site award at any given time.
Proposal Preparation and Submission Instructions
A. Proposal Preparation Instructions
- Letters of Intent: Not required
-
Preliminary Proposals: Submission of Preliminary Proposals is required. Please see the full text of this solicitation for further information.
-
Full Proposals:
- Full Proposals submitted via Research.gov: NSF Proposal and Award Policies and Procedures Guide (PAPPG) guidelines apply. The complete text of the PAPPG is available electronically on the NSF website at: https://www.nsf.gov/publications/pub_summ.jsp?ods_key=pappg.
- Full Proposals submitted via Grants.gov: NSF Grants.gov Application Guide: A Guide for the Preparation and Submission of NSF Applications via Grants.gov guidelines apply (Note: The NSF Grants.gov Application Guide is available on the Grants.gov website and on the NSF website at: https://www.nsf.gov/publications/pub_summ.jsp?ods_key=grantsgovguide).
B. Budgetary Information
-
Cost Sharing Requirements:
Inclusion of voluntary committed cost sharing is prohibited.
-
Indirect Cost (F&A) Limitations:
Membership fees received by the Center are considered program income. At least 90% of the IUCRC program income must be used to support direct costs of the research, and up to 10% may be used to support indirect costs.
NSF award funds are subject to an institution’s federally-negotiated indirect cost rate. See Special Award Conditions.
-
Other Budgetary Limitations:
Other budgetary limitations apply. Please see the full text of this solicitation for further information.
C. Due Dates
-
Preliminary Proposal Due Date(s) (required) (due by 5 p.m. submitting organization’s local time):
July 07, 2020
September 16, 2020
March 10, 2021
Second Wednesday in March, Annually Thereafter
September 08, 2021
Second Wednesday in September, Annually Thereafter
Preliminary proposals are required prior to submission of planning grants. Submitters seeking a waiver of the planning grant stage must submit the waiver request as a preliminary proposal.
-
Full Proposal Target Date(s):
September 08, 2020
December 16, 2020
June 09, 2021
Second Wednesday in June, Annually Thereafter
December 08, 2021
Second Wednesday in December, Annually Thereafter
Proposal Review Information Criteria
Merit Review Criteria:
National Science Board approved criteria. Additional merit review criteria apply. Please see the full text of this solicitation for further information.
Award Administration Information
Award Conditions:
Additional award conditions apply. Please see the full text of this solicitation for further information.
Reporting Requirements:
Additional reporting requirements apply. Please see the full text of this solicitation for further information.
I. Introduction
An IUCRC operates as a consortium integrating industry, government, and academia. The industrial community includes major corporations, middle market companies, small businesses and startups; public participants may range from local governments to divisions of federal agencies. These stakeholders partner to advance critical technologies from early stage research to the marketplace (Figure 1). The membership fees support research projects conducted by university faculty and students. NSF provides funding for operations and a governance framework for membership, operations, and evaluation.
IUCRCs engage in basic research that is considered “pre-competitive.” This means that the research is intended for publication through avenues available for academic and scientific research. Pre-competitive research allows industry Members who might be competitors in the commercial marketplace to work collaboratively within an IUCRC to help shape its research activities and focus. IUCRCs are expected to work on research that is transformative and helps reshape the frontiers of knowledge of industry relevance.
An IUCRC provides the infrastructure for training a diverse, high-tech workforce, including through the recruitment of students and faculty of populations historically underrepresented in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) disciplines. Furthermore, it provides a forum for startups to engage with industry and develop a rich network of corporate, academic, and public resources to accelerate technology translation.
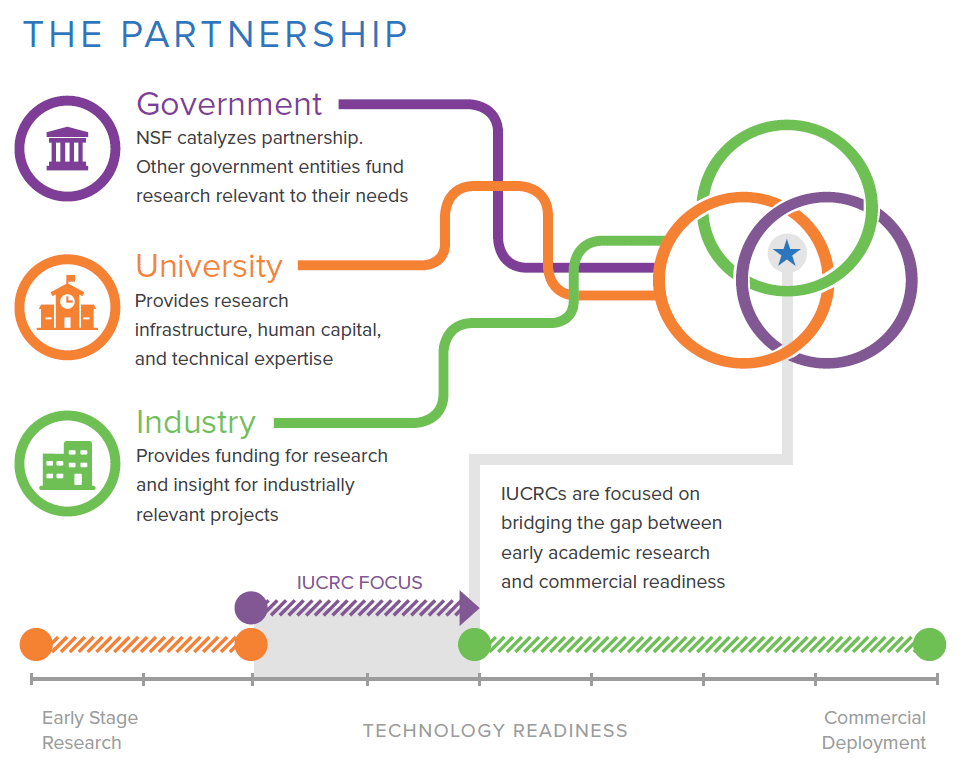
Figure 1. The IUCRC’s role in translating research from concept to commercialization.
II. Program Description
A. Program Architecture
An NSF supported Industry-University Cooperative Research Center (“IUCRC” or “Center”) is a consortium comprising one or more University “Sites” and a number of Member organizations who pay membership fees that support the Center’s research costs and activities. It consists of the following main elements:
- University Sites: Universities/Institutions of Higher Education (IHEs) participating in an IUCRC, either as a Lead Site or a Partner Site.
- Members: Companies (large and small businesses, startups, for-profit and non-profit entities) and government agencies (federal, state and local) who pay membership fees, recognized as Program Income (https://www.nsf.gov/publications/pub_summ.jsp?ods_key=pappg); please see Section VIII.D.4: Program Income, to become a Member of the IUCRC.
- Industry Advisory Board (IAB): Representatives from the Member organizations who participate actively in guiding and supporting the IUCRC’s mission and vision, research roadmap, and related programs.
- NSF: NSF provides funding for administrative costs, program oversight, and a governance framework to manage membership, operations, and evaluation.
1. Center creation
Creating an IUCRC requires a strong desire to build public-private partnerships, knowledge of pressing industry needs, a capable leadership team, access to students, and research infrastructure. To launch an IUCRC, the university team must identify the research needs of an economic sector under transformation, confirm alignment of university leadership, secure financial commitments from industry players, and establish an effective governance framework.
NSF considers each IUCRC a nationwide investment and encourages the formation of multi-university (i.e., multi-site) Centers, each of which should address distinct, unique needs. A prospective Principal Investigator (PI) should confirm that a proposed Center does not overlap with existing Centers in the Directory (https://iucrc.nsf.gov/centers/); in the event of overlap with an existing IUCRC, the PI should explore the possibility of joining that Center.
During Center creation, NSF funds a year-long Planning Grant process, through the standard NSF merit review process, to train prospective Center leaders on best practices for establishing and maintaining a successful IUCRC. The path to Center creation (Figure 2) involves several distinct steps, including planning, training, customer discovery and Member recruitment, and ultimately leading to the submission of a Phase I IUCRC proposal.

Figure 2. The path to IUCRC creation from conception to award.
2. Center lifecycle
IUCRCs progress from inception through each stage, ultimately with the goal of becoming a Graduated Center, which is defined as successfully completing the highest IUCRC Phase available under the solicitation in which it was funded, continuing to meet or exceed the minimum membership and membership fee total cash requirements, and continuing to use the NSF governance framework. (Figure 3). To align with the accelerated pace and evolution of industry research, NSF offers new Centers two Phases of funding (five years each). This includes two funding level options within Phase II (i.e., Phase II and Phase II+).
Active Phase I Centers, established under this or prior solicitations and transitioning to Phase II, will be subject to the model described in Figure 3 (i.e., Phase II or Phase II+). Active Phase II Centers (funded under prior solicitations) may elect to progress to Phase III under this solicitation.

Figure 3: IUCRC evolution and funding paths offered in this solicitation.
3. Center funding model
An IUCRC conducts research under the leadership and guidance of an Industry Advisory Board (IAB) to manage project selection, fund projects, and share results. To qualify for NSF support, a Center must meet specific requirements in both membership and membership fees (see Table 1). The Center may offer two membership fee levels (Full and Associate). See Section B.1 below for definitions of terms and Section VII.B for the Special Award Conditions.
|
|
Planning |
Phase I |
Phase II |
Phase II+ |
Phase III1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Multi-Site Center (Number of Sites = N) |
|||||
|
Annual NSF Site Funding2 |
$20,000 |
$150,000 |
$100,000 |
$150,000 |
$50,000 |
|
Annual Minimum Membership |
n/a |
3 x N |
4 x N |
6 x N |
5 x N |
|
Minimum membership fee total3 |
n/a |
$150,000 x N |
$200,000 x N |
$300,000 x N |
$250,000 x N |
|
Single-Site Center |
|||||
|
Annual NSF Site Funding |
$20,000 |
$150,000 |
$100,000 |
$150,000 |
$50,000 |
|
Annual Minimum Membership |
n/a |
8 |
8 |
12 |
8 |
|
Minimum membership fee total3 |
n/a |
$400,000 |
$400,000 |
$600,000 |
$400,000 |
|
1 Phase III funding is an available option only for active Phase II Sites funded under prior solicitations. 2 Additional flexibility in specifying a Center’s NSF budget is described in Section V.A Budget Allocations for Center Operations and Management. 3 Does not include in-kind contributions. |
|||||
B. Center Structure and Membership
1. Terms and Definitions
Organizations, Entities, and Structure:
- Site: A University/Institutions of Higher Learning participating in an IUCRC.
- Lead Site: The Site with administrative and management responsibility for the Center-wide activities such as Member recruitment and retention, IAB meetings organization, collection and allocation of membership fees and other program income, and managing Center operations. The Lead Site administrative role and associated expenses are defined and budgeted in a required Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) executed by all Sites.
- Partner Site: A participating Site that is not the Lead Site.
- External Collaborator: An external entity or individual required to address a critical research need, subject to NSF and IAB approval and paid for from Program Income.
- Industry Advisory Board (IAB): An advisory body composed of representatives from the Center’s member organizations. The IAB elects a Chair and Vice-Chair and makes recommendations on (a) the Center’s research projects, (b) the apportionment of resources to these research projects, and (c) Bylaws. The IAB ensures that the university team is conducting research of relevance to the industry Members. The IAB helps to refine the mission, vision, and research roadmap for the Center.
- Academic Leadership Team: A team comprising the PIs and co-PIs of all Sites, with responsibility for overseeing and carrying out the IAB-recommended research activities and ensuring Center success.
- Sponsored Projects Office (SPO) (or equivalent): University administrative unit at the Lead Site that provides an annual Center membership certification form (https://iucrc.nsf.gov/universities/solicitation/SRO-membership-certification/).
- Academic Policy Committee: University unit at each Site composed of members of the institution’s administration (for example, Vice President of Research, Dean, Associate Dean of Research, Vice Dean of Innovation, Department Chair, etc.). Examples of this committee’s responsibilities include managing Conflict of Interest or personnel performance issues within the Center/Site.
- Phase: A Phase is one of two 5-year sequential stages of development and NSF funding. Phases under this solicitation may be I, II or II+, or III. Phases II and II+ are not consecutive but rather mutually exclusive options for Phase II with different NSF funding levels as a function of the level of industry participation (Table 1). Phase III is available only for active Phase II Centers funded under prior solicitations. A Planning Grant does not qualify as a Phase. A Phase applies to the entire Center; individual Sites cannot be in different Phases in the same Center.
- Site addition: Centers may expand to include participation from additional University Sites, in order to enhance research capabilities and impact. A new Site may join an existing Center if it can demonstrate that it can meet NSF membership requirements for the expanded Center and its proposal must undergo the merit review process. A Site joins an IUCRC in the Center’s current Phase, with an award limited to the remaining duration of the active Center.
Personnel and Roles:
- Center Director: The PI of the Center Lead Site proposal; oversees Center operations and management, Center research programs and serves as the Center’s key point of contact.
- Site Director: The PI for a Partner Site; serves on the Academic Leadership Team, manages the Site’s research program, and serves as the Site’s point of contact for Site-related activities.
- Industry Liaison Officer: This position is typically associated with the Lead Site and has the primary responsibilities for communicating Center value, identifying and recruiting new Members, and building and maintaining existing industry relationships. This position is highly recommended but is not required if the Center leadership has sufficient time and experience to carry out this additional role. Partner Sites are expected to provide partial support for this position by contributing funds as described in Section V.A Budget Allocations for Center Operations and Management for detailed information.
Membership Terms:
- Fees: The annual financial commitment, payable in cash (not in-kind contributions), contributed by a Member organization.
- Member: Fee-paying organization that signs the IUCRC membership agreement.
- Full Member: A Member that pays the full membership fee, and has one full voting right.
- Associate Member: A Member that pays one-half of the Full Member fee, and has one-half of a voting right.
- Affiliates: An entity providing approved in-kind contribution, or an entity involved in the Center with conflict-of-interest that may wish to support the Center by contributing funds (at the associate membership or full membership level). Affiliates do not count toward membership fees, have no voting rights and do not have exclusive or non-exclusive, royalty-free license access to the Center Intellectual Property.
- Membership (Number of Equivalent Full Members): Equivalent Full memberships are counted by aggregating the Full and Associate memberships to determine compliance with the solicitation requirements (Table 1). For example, a Center with 4 Full Members and 2 Associate Members has 5 Equivalent Full Members.
- Membership Fees: The total membership fees collected. The fees of Full and Associate Members are aggregated into the membership fee total to determine compliance with the solicitation requirements (Table 1).
- Program Income: All funds contributed by Members are classified as Program Income. At least 90% of the IUCRC Program Income must be used to support the direct costs of research, and up to 10% may be used to support indirect costs. For additional information, see https://www.nsf.gov/pubs/policydocs/pappg22_1/pappg_8.jsp#VIIID4.
Note: The Center’s Industry Advisory Board (IAB) may vote on the allocation of Member funds to support direct costs other than research to meet the Center’s specific needs in support of its mission. The Center may bring specific requests to the IAB for a vote and recommendations.
- Voting rights: Voting rights are assigned based on Membership Level. Full Members are allotted one voting right for one membership fee. A Member may acquire multiple memberships, but membership contributions in excess of two full memberships are capped at two voting rights. Associate Members pay a reduced (one-half) membership fee, and thus have 0.5 voting rights.
- Center Research: The Center Program Income is directed toward the research activities, as recommended by the IAB, and conducted at the Sites by the university researchers (faculty, graduate students, post graduate students, etc.). Membership fees are classified as Program Income.
Agreements and Policies:
- Memorandum of Understanding (MOU): A Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) between Sites in the Center must be negotiated such that the Lead Site’s administrative role and associated expenses are defined and budgeted. The Lead Site serves as a central collection and distribution site for all membership fees and Member-related Program Income, including funds allocated to research projects executed at Partner Sites. All Sites execute the same MOU.
- NSF Budget Allocations: NSF funding for a university Site is intended to support operations, management, and administration at both the Center and Site levels. Site budgets must allocate NSF funds to the Lead Site for Center operations (Section V.A).
- Bylaws: The Center Bylaws define the operating procedures that will be applied to govern the operations of the Center. These operating procedures are approved by the IAB and the Academic Leadership Team. Bylaws are reviewed by NSF for acceptability with the IUCRC program.
- IUCRC Membership Agreement: All Center Members sign one common agreement. The common template agreement to be adopted is published on the NSF website at https://iucrc.nsf.gov/industry/joining-a-center/membership-agreement/.
- Conflicts of Interest: A Conflict of Interest policy must be implemented for the Center and presented in the Bylaws, to address companies or entities for which: (1) a researcher involved in the Center is the founder, president, a key officer or a majority shareholder, or (2) the organization is in any way financially affiliated with any of the universities that are part of the Center (e.g., university foundation, university subsidiary).
2. Strategy and Governance
Centers are characterized by having the following:
Strategy:
- A research scope unique among existing IUCRCs and representing the shared interests of the Center research team and IAB;
- A portfolio of fundamental and pre-competitive collaborative research projects of interest to multiple IAB Members;
- A mechanism to share project outcomes with all Center Members;
- A plan for attracting new Members, retaining existing Members, and building strong relationships between the Center research team and IAB;
- A plan to establish a diverse mix of industry Member organizations, including companies (large and small), startups, non-profit organizations, government agencies, and/or other interested non-academic entities;
- Strong representation by all Sites in Center research activities, with an emphasis on projects requiring engagement and collaboration among multiple Sites;
Governance
- A priority-driven ranking mechanism by which the IAB can recommend funding. (A voting method that allows one IAB Member to independently fully fund its project(s) of choice is viewed as supporting contract work and is disallowed under the IUCRC framework);
- Documentation of Center goals and objectives, created jointly by the Center research team and the IAB, and an associated research roadmap;
- A uniform membership agreement conforming to the NSF IUCRC-wide model (https://iucrc.nsf.gov/industry/joining-a-center/membership-agreement/ );
- A Memorandum of Understanding articulating the financial and operational responsibilities of each Site;
- A set of IAB-approved Center Bylaws to document Center operating procedures, consistent with the IUCRC membership agreement and model, including a process to reorganize leadership at the Center or Site level if deemed necessary by the NSF and IAB.
3. Eligibility for Membership
Members are critical to effective Center functioning, as they vote to recommend projects of mutual interest that will form the research portfolio. Furthermore, they define which projects are chosen, fund research, and monitor Center performance.
Members may be companies (large and small), startups, non-profit organizations, government agencies, and/or other interested non-academic entities. To ensure research translation into commercial uses for societal impact, NSF encourages Centers to recruit IAB Members primarily from the private sector. The following eligibility requirements apply:
- Members must have an Employer Identification Number (EIN) issued by the U.S. Internal Revenue Service. Exceptions to this requirement must be approved in writing by the cognizant Program Officer.
- Two divisions within the same parent organization count as distinct Members only if each division has a unique EIN.
- An entity must submit a signed IUCRC membership agreement (See Agreements and Policies Section II.B.1) to the Lead Site SRO and pay an annual membership fee.
- U.S. federal agencies, Federally Funded Research and Development Centers (FFRDCs), national laboratories, and state and local government agencies may become Members (https://iucrc.nsf.gov/government/). Distinct entities within a government agency qualify as distinct Members (e.g., Army CERDEC and Army Research Laboratory).
- An entity financially connected with any of the Sites (e.g., a university foundation or subsidiary) may become an Affiliate Member of that Center. The entity's membership fee counts as Program Income. The entity and its membership fees do not count toward Center minimum membership requirements. The entity does not have IAB voting rights. Any Center-supported faculty involved in an Affiliate Member company must provide written notice to the Center Director and the Center IAB of their involvement in the company and must comply with conflict of interest policies of their institution.
- An entity or company in which a Center faculty member is the founder, president, key officer, or principal shareholder, may become an Affiliate Member of the Center. The entity's membership fee counts as Program Income. The entity and its membership fees do not count toward Center minimum requirements. The entity does not have IAB voting rights.
4. Membership structure
- Categories and memberships: A Center may have three membership categories: Full, Associate, and Affiliate. Full Members pay 100% of the fee, Associates pay 50% of the fee, and Affiliate Members may provide in-kind contributions or pay fees that count as Program Income but that do not count toward meeting membership fee requirements (Table 1). The distinct number of Associate Members can be added together to create an Equivalent Full Membership (e.g., two Associate Members at 50% are equivalent to one Full membership).
- Voting rights: A full Member earns one vote. Voting is pro-rated based on the paid membership fee. An organization may buy multiple memberships in a Center, but contributions exceeding two full memberships are capped at two votes. Affiliate Members do not have voting rights.
- In-kind contributions: An in-kind contribution by an Affiliate Member, such as (but not limited to) equipment or instruments, must be approved by IAB and does not qualify toward meeting minimum membership fee total cash contribution requirements set by NSF.
Example: As an example, in Table 2 a Phase I Center is shown that has two Sites offering full and associate memberships with fee levels of $50,000/$25,000 respectively, as well as affiliate memberships. This Center must have at least 6 full memberships (3 x 2 Sites) and $300,000 ($150,000 x 2 Sites) in total membership fees cash contributions during each year of Phase I. The Center has $625,000 of Program Income, 9.5 voting rights, 7 full memberships, and $525,000 in eligible membership fees.
|
Organization
|
Program Income from Membership Fee |
Member Type
|
Voting Rights
|
Qualification towards |
Comments |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Membership (number of equivalent full Members) | Member-ship Fees | |||||
|
Company A |
$50,000 |
Full |
1 |
1 |
$50,000 |
|
|
Company B |
$100,000 |
Full |
2 |
1 |
$100,000 |
|
|
Company C |
$150,000 |
Full |
2 |
1 |
$150,000 |
Cap of 2 votes for any Member |
|
Company D |
$25,000 |
Associate |
0.5 |
0.5 |
$25,000 |
|
|
Company E |
In-Kind Contribution |
Affiliate |
0 |
0 |
$0 |
In-kind does not count toward membership |
|
Company F |
$75,000 |
Full |
1.5 |
1 |
$75,000 |
|
|
Startup G |
$25,000 |
Associate |
0.5 |
0.5 |
$25,000 |
|
|
PI-linked startup H |
$50,000 |
Affiliate |
0 |
0 |
$0 |
PI is conflicted |
|
Non-profit I |
$50,000 |
Full |
1 |
1 |
$50,000 |
|
|
University-affiliated non-profit J |
$50,000 |
Affiliate |
0 |
0 |
$0
|
Site is conflicted |
|
Government agency K |
$50,000 |
Full |
1 |
1 |
$50,000 |
|
|
Total |
$625,000 |
|
9.5 |
7.0 |
$525,000 |
|
C. Center Stages and Evolution
1. Planning Grant
Each proposed Site seeks funding from NSF for formal planning activities in a preliminary proposal briefly describing the Center concept, each Site’s role, and the prospective companies and government agencies interested in the Center. After evaluation, NSF encourages or discourages submission of a full proposal for a Planning Grant. IUCRC Planning Grantees are required to participate in the following activities: 1) a Boot Camp to learn how to create a sustainable Center; and 2) a two-day Planning Workshop organized by the Grantees, engaging potential IAB Members in a discussion of the proposed Center focus, its value propositions, potential research projects, and a research roadmap of strongest interest to industry Members. Please note that the Planning Grant proposals described in this solicitation are a solicitation-specific project category and are separate and distinct from the Planning type of proposal described in Chapter II.E.1 of the PAPPG. When preparing a Planning Grant proposal in response to this solicitation, the “Research” type of proposal should be selected.
a) Planning Grant Boot Camp
NSF oversees and runs the Boot Camp to teach an effective planning process, including Member discovery and recruitment, as well as best practices in Center operations. Attendance is mandatory. Key participants include the Lead Site PI (i.e., Center Director), the PIs of Partner Site awards (Site Directors), the Center Industry Liaison Officer (if identified), and other key Center team members.
b) Planning Workshop
A Planning Grant funds a two-day workshop for Center faculty to engage prospective companies and government agencies (i.e., potential Members) to discuss the IUCRC model, proposed focus, and value proposition. Workshop outcomes include: 1) A research roadmap and a portfolio of proposed innovative projects addressing significant industry challenges; 2) A sufficient number of financial commitments from prospective Members to meet or exceed Phase I membership and membership fee total requirements; and 3) A team of faculty, staff, and university administrators committed to leading a transformative research program.
c) Waiver
A potential IUCRC consortium that has already completed planning activities and achieved the Planning Grant Workshop outcomes outlined above may seek a Planning Grant waiver (subject to NSF approval) to accelerate Center formation and bypass the NSF-funded Planning Grant stage.
2. Phase I
For new IUCRCs created and funded under this solicitation, NSF provides support to Centers/Sites for a five-year Phase I award. The Phase I award is required to apply for Phase II.
3. Phase II
A Phase II grant allows a Center to grow and diversify its membership and research portfolio. In the final year of Phase I, all of the Sites apply as a group for Phase II (years 6-10 of the Center). The Center must demonstrate that it met NSF grant requirements during Phase I and can meet the minimum Phase II membership and funding commitment requirements.
Phase II has two mutually-exclusive funding designations – Phase II and Phase II-Plus (Phase II+). The choice of Phase II or Phase II+ must be determined at the time of proposal submission. Transitions from Phase II to Phase II+ and vice versa within the Phase II award period is prohibited.
- Phase II:
Phase II is for an N-Site Center that seeks to maintain an annual minimum equivalent full membership level of 4 Members x N and annual minimum membership fees of $200,000 x N. The Center may request an NSF budget of $100,000 per Site per year. Single site Phase II Centers must have an annual minimum equivalent full membership level of 8 Members, annual minimum membership fees of $400,000 and may request an NSF Budget of $100,000 per year.
- Phase II+:
Phase II+ is for an N-Site Center that seeks to maintain an annual minimum equivalent full membership level of 6 Members x N and annual minimum membership fees of $300,000 x N. The Center may request an NSF budget of $150,000 per Site per year. Single site Phase II+ Centers must have an annual minimum equivalent full membership level of 12 Members, annual minimum membership fees of $600,000, and may request an NSF Budget of $150,000 per year.
Note: Phase I IUCRCs planning to submit a Phase II+ need to achieve a substantial ramp up of membership during Phase I to be in position to meet the higher membership requirements of the Phase II+. For example, N-Site Phase I Centers should seek to reach 5XN memberships by year 5 to be in a stronger position to meet or exceed the membership requirements of the Phase II+.
4. Phase III (restricted availability)
Active Phase II Centers currently funded under prior IUCRC program solicitations may compete for an additional five years of Phase III funding. See Table 1 for further details and requirements.
Phase III is available only to active Phase II Centers funded under prior solicitations and may last five years. A Center must be in the last year of Phase II as per the solicitation under which it was funded. A Site that has been added in Phase II under this solicitation, to an existing center (that has sites funded under prior solicitations), will be permitted to apply for Phase III if the center chooses to transition to Phase III as allowed in this solicitation.
A Phase III, Phase II, or Phase II+ Center funded under this solicitation is expected to reach self-sustainability at the end of the award period.
5. Addition of a Site to an existing Center
A Site joining an existing NSF-funded Center will submit a full proposal to NSF to join the current Phase of the Center and is limited to the Center’s remaining duration. For example, if a Center is in year two of Phase II, the Site may only apply to join that Center as a Phase II Site (not Phase I, even if it is that Site’s first year) for the remaining 3 years of Phase II. The new Site must contribute to the requisite new Member number and incremental financial commitment to support the requirements (Table 1), as modified to reflect the new Site addition; evidence of this capability must be presented with the new Site’s Full Proposal. A new Site’s budget request is limited per Table 1.
Example: A two-Site Phase I Center with a $50,000 membership fee and 7 qualifying memberships summing to a membership fee total of $350,000. The Center exceeds the required member number and fees (i.e., 6 Members and $300,000 in fees; see Table 1). However, if the Center adds a new Site, the Center must demonstrate 9 memberships and fees summing to $450,000. The new Site proposal must therefore coordinate with the Lead Site/Center Director to identify and include financial commitment letters from at least 2 new Members providing an additional $100,000 or more.
The new Site must execute the same MOU as the Center’s other Sites, to contribute to funding the Lead Site’s administrative costs.
6. Graduated Centers
A Center may continue to appear in the active IUCRC portfolio as a Graduated Center if it successfully completed the highest IUCRC Phase available under the solicitation in which it was funded, continues to meet or exceed the NSF requirements of that Phase as specified in that solicitation, and continues to use the NSF governance framework. To be registered as a Graduated Center, the Center Director must submit a report annually to NSF via email to IUCRC@nsf.gov for review.
D. Supplemental funding opportunities
Active supplemental funding opportunities are described in greater detail here: https://iucrc.nsf.gov/universities/solicitation/funding/
All requests should be discussed with the cognizant Program Officer and approved prior to submission as not all NSF Directorates support all supplement types.
1. Supplements to Enhance IUCRC Training and Education
A Center may advance its training and education mission via multiple supplemental funding opportunities (limited to the availability of funds and other programmatic considerations). Available supplements include:
- Non-Academic Research Internships for Graduate Students (INTERN): Support graduate students in research in non-academic settings, including company and government laboratories, to enhance student career potential and provide work experience outside of academia; typically, up to $55,000
- Research Experience for Undergraduates (REU): Support undergraduate student involvement in research; typically, up to $8,000 per student
- Research Experiences for Teachers (RET): Support research participation by K-12 teachers and community college instructors; typically, up to $10,000 per teacher
- Veterans Research Supplement (VRS): Support research participation by undergraduate or graduate students, K-12 STEM teachers, or community college instructors and students who have served in active duty with the U.S. armed forces; typically, up to $10,000 per veteran
2. International Supplements
Collaboration with leading international research entities can further advance a Center’s goals. With prior approval of the IAB and NSF, a Center may submit a supplemental funding request to foster collaborative work with an international partner; the proposal should include details on:
- Description of how the IUCRC would interact with the international research Site;
- Description of the proposed research projects;
- Description of the existing infrastructure to enable collaboration;
- Evidence that the international research entity has adequate industry partner funding to support the proposed projects, at a level of research activity comparable to what is ongoing at the U.S. IUCRC’s sites;
- Documentation that the international Site has been/will be established following the framework of the IUCRC governance model;
- A memorandum of understanding (MOU) between the NSF IUCRC and the international Site addressing IP rights, copyrights, publication delays, and participation of the international Site industry members in the IUCRC Industry Advisory Board activities; and
- A letter from the IUCRC IAB endorsing the international collaboration and the above mentioned MOU.
For IUCRCs with international collaborations, NSF will consider: intellectual merit of the collaboration with the international partner(s), benefits to be realized from the international partner's expertise and specialized skills, facilities, Sites, and/or resources of the international counterpart, and active research engagement of IUCRC-based students and early-career researchers, as appropriate.
This collaboration and its funding are active during the Phase in which the international supplement request was approved. Each IUCRC is limited to one annual international supplement request, not to exceed $25,000. Funds are to be used only for expenses related to the international activity, such as research visits by Center faculty and students to the international site for research and collaborative activities. NSF funds may not be used by foreign partners.
III. Award Information
Anticipated Type of Award: Standard Grant or Continuing Grant
Estimated Number of Awards: 10
2 to 8 full Center awards and 4 to 6 Planning Grant awards annually.
Anticipated Funding Amount: $20,500,000
Individual award sizes (total costs):
$20,000 for Planning Grants
$150,000 per year for Phase I
$100,000 per year for Phase II
$150,000 per year for Phase II+
$50,000 per year for Phase III
Planning Grants are intended to be awarded as standard grants. All Center Site Grants will be awarded as Continuing Grants.
Estimated program budget, number of awards and average award size/duration are subject to the availability of funds.
IV. Eligibility Information
Who May Submit Proposals:
Proposals may only be submitted by the following:
- Institutions of Higher Education (IHEs) - Two- and four-year IHEs (including community colleges) accredited in, and having a campus located in the US, acting on behalf of their faculty members. Special Instructions for International Branch Campuses of US IHEs: If the proposal includes funding to be provided to an international branch campus of a US institution of higher education (including through use of subawards and consultant arrangements), the proposer must explain the benefit(s) to the project of performance at the international branch campus, and justify why the project activities cannot be performed at the US campus.
Who May Serve as PI:
The Principal Investigator (PI) on a proposal must be a tenured faculty member. Requests for waivers to allow non-tenured faculty or research staff to serve as PI must be submitted in writing to the cognizant Program Officer by the PI's supervisor (e.g., Department Chair or Dean) in advance of proposal submission. Further, written approval from the cognizant Program Director is required prior to proposal submission and should be included as a Single Copy Document in the proposal. The PI must act as the initial Site Director. A PI/Co-PI can have only one active IUCRC Site award at any given time.
Limit on Number of Proposals per Organization:
There is no limit to the number of proposals an eligible organization may submit to this program as long as each proposal pertains to a different IUCRC.
Limit on Number of Proposals per PI or co-PI:
PIs and Co-PIs can only submit one proposal per submission period. A PI/Co-PI can have only one active IUCRC Site award at any given time.
Additional Eligibility Info:
- Preliminary proposals are required prior to submission of planning grants. Submitters seeking a waiver of the planning grant stage, must submit the waiver request as a preliminary proposal.
- Planning Grant. A PI must submit a preliminary proposal to be eligible to submit a Planning Grant Full Proposal.
- Phase I proposal. Consortia who have successfully completed the Planning Grant process (including the Boot Camp training and Planning Workshop) are eligible; alternatively, consortia who have obtained an NSF-approved Planning Grant waiver are also eligible.
- Phase II or Phase II+ proposals. Active Phase I Centers are eligible.
- Phase III proposals. Active Phase II Centers funded under prior solicitations are eligible.
A Proposal reviewed under this solicitation or under NSF 17-516 that was previously declined, may be revised and resubmitted for further consideration in response to the requirements of this Solicitation.
V. Proposal Preparation And Submission Instructions
A. Proposal Preparation Instructions
Preliminary Proposals (required): Preliminary proposals are required and must be submitted via Research.gov, even if full proposals will be submitted via Grants.gov.
Preliminary proposals are required prior to submission of planning grants. Submitters seeking a waiver of the planning grant stage must submit the waiver request as a preliminary proposal. Page limits specified here are maximum. Each institution must submit its own Preliminary Proposal.
This solicitation contains the information needed to prepare a proposal and refers to specific sections of the PAPPG only when necessary. The instructions in this solicitation take precedence over instructions in the PAPPG in the event of deviations.
Preliminary Proposal Set-Up: Select "Prepare New Preliminary Proposal" in Research.gov. Search for and select this solicitation title in Step One of the Preliminary Proposal wizard. Select "Single proposal (with or without subawards). Separately submitted collaborative proposals will be returned without review.
A. Planning Grant Preliminary Proposal Title
Project Title Format: IUCRC Preliminary Proposal [Planning Grant, Planning Grant Waiver request] [Site Name]: Center for [Center name] [Center Acronym]
Designations inside the first set of square brackets indicate the type of proposal submitted (Planning Grant or Planning Grant Waiver request). [Site Name] is the name of the submitting institution. The Center name should briefly describe the Center’s research focus, which should be followed by an acronym (e.g., "IUCRC Preliminary Proposal Planning Grant Red River University: Center for Cloud Computing and Innovation (CCI)”).
Award size and duration requested:
- Planning Grant: Up to $20,000 for 12 months.
- Planning Grant Waiver: Up to $750,000 for 60 months for a site in a Phase I Center.
B. Biographical Information for Preliminary Proposals (2 pages)
Provide one paragraph in prose for each member of the research team for the entire Center.
C. Project Description for Preliminary Proposals (2 pages)
Start with the project title and type (e.g. Planning Grant or Planning Grant Waiver request). Discuss:
- The proposed Center’s vision and mission;
- Key unmet industry research needs driving Center creation;
- Economic importance of the research area;
- Demonstration of Center’s uniqueness and differentiation from other IUCRCs and NSF-funded Centers;
- Pre-existing research partnerships between the Sites related to the Center’s focus;
- List of potential research thrust areas and planned collaborative, synergistic, and Center-wide contributions by the Site;
- List of prospective Members, statement of who has already been contacted, and the estimated level of interest; and
- For each Site include specific information regarding its faculty, capabilities, and resources to be contributed to the Center.
D. Supplementary Documentation for Planning Grant Waiver Requests Only (3 pages)
Describe the relevant Center/Site planning events/workshops/activities involving active industry engagement to date. List each organization committing to join the Center and specify the amount and duration of its annual financial commitment.
Decisions on Planning Grant Preliminary Proposals and Planning Grant Waiver Requests
Submitting PIs of a Preliminary Proposal will receive an Encourage or Discourage decision from NSF. NSF’s Encourage/Discourage decision made on the preliminary proposal or a planning grant waiver is advisory only. This means that PIs of both favorably and unfavorably reviewed Preliminary Proposals are eligible to submit full proposals.
An encourage finding indicates that the proposal appears to be responsive to this solicitation and is a candidate for full proposal merit review. A discourage finding indicates that the project did not respond to the solicitation and has a low likelihood of funding support.
Full Proposal Preparation Instructions: Proposers may opt to submit proposals in response to this Program Solicitation via Research.gov or Grants.gov.
- Full Proposals submitted via Research.gov: Proposals submitted in response to this program solicitation should be prepared and submitted in accordance with the general guidelines contained in the NSF Proposal and Award Policies and Procedures Guide (PAPPG). The complete text of the PAPPG is available electronically on the NSF website at: https://www.nsf.gov/publications/pub_summ.jsp?ods_key=pappg. Paper copies of the PAPPG may be obtained from the NSF Publications Clearinghouse, telephone (703) 292-8134 or by e-mail from nsfpubs@nsf.gov. The Prepare New Proposal setup will prompt you for the program solicitation number.
- Full proposals submitted via Grants.gov: Proposals submitted in response to this program solicitation via Grants.gov should be prepared and submitted in accordance with the NSF Grants.gov Application Guide: A Guide for the Preparation and Submission of NSF Applications via Grants.gov. The complete text of the NSF Grants.gov Application Guide is available on the Grants.gov website and on the NSF website at: (https://www.nsf.gov/publications/pub_summ.jsp?ods_key=grantsgovguide). To obtain copies of the Application Guide and Application Forms Package, click on the Apply tab on the Grants.gov site, then click on the Apply Step 1: Download a Grant Application Package and Application Instructions link and enter the funding opportunity number, (the program solicitation number without the NSF prefix) and press the Download Package button. Paper copies of the Grants.gov Application Guide also may be obtained from the NSF Publications Clearinghouse, telephone (703) 292-8134 or by e-mail from nsfpubs@nsf.gov.
See PAPPG Chapter II.D.2 for guidance on the required sections of a full research proposal submitted to NSF. Please note that the proposal preparation instructions provided in this program solicitation may deviate from the PAPPG instructions.
Full proposals are required for Planning Grants, Site Additions, and all Phases (Phase I, II, II+, and III) to this solicitation. Each Site must submit its own individual full proposal for any IUCRC proposals.
A. Cover Sheet
Project Title Format: IUCRC [Planning Grant, Phase I, Phase II, Phase II+, Phase III] [Site Name]: Center for [Center name] [Center Acronym].
Designations inside the first set of square brackets indicate the type of proposal being submitted, and only one of the options therein should be selected. [Site Name] is the name of the submitting institution. The Center name should briefly describe the Center’s research focus, which should be followed by the Center acronym (e.g., "IUCRC Phase II+ Red River University: Center for Cloud Computing and Innovation (CCI)”).
Duration:
- Planning Grant: 12 months.
- Phases I, II, II+, and III: 60 months.
- Site addition: Center’s remaining grant duration in its current Phase.
B. Project Description (20 pages maximum)
The first 5 to 10 pages are for “Center Focused Content,” and must be identical for each Site among a multi-Site Center proposal. The remaining 10 to 15 pages are “Site-Specific Content” identifying specific contributions, capabilities, and uniqueness at each Site.
The first 5 to 10 pages of the “Center Focused Content” include:
- Overview: State the mission and vision; national strategic importance and uniqueness; unmet/underserved pre-competitive research needs to be addressed.
- Broader Impacts: Discuss the projected societal impact of the Center’s research, education, and outreach activities.
- Center Composition: Identify the Lead Site and Partner Sites. How do each Site’s capabilities contribute to realize the Center’s mission and vision?
- Leadership Team: Discuss the background, qualifications, and management experience and capabilities of the key team members (one prose paragraph per team member).
- Industry Partners: Discuss financially committed and prospective (uncommitted) Members considering joining the Center, and your proposed membership scheme and pricing structure (i.e., Full/Associate Members, etc.).
- External Collaborators (research contractors): If applicable, describe any external collaborators projected to help with the Center’s success. Do not include IAB Members, Site personnel, or others engaged with the Center as university faculty, staff, or students.
- Industry Engagement Plan: Discuss plans for customer discovery and industry recruitment and retention to engage a relevant and diverse mix of industry Members, including companies (large and small), startups, non-profit organizations, government agencies, and/or other interested non-academic entities. Discuss the plans to actively engage industry Members in ongoing Center activities.
- Outreach and Communication: Discuss the communications strategy to reach prospective Members, academic partners and the general public. Discuss efforts to grow industry participation in the Center.
- Operations: Discuss the management plan, organizational structure, operational procedures, financial plan, and risk management associated with the Center.
- Sustainability Plan. Describe the Center’s strategy for growing and achieving self-sustainability by the time of graduation (i.e., 10 years for the new model described in this solicitation, or the remaining years for active Phase II Centers funded under prior solicitations).
- Results from Prior Center Accomplishments: For Phase II, II+ and Phase III proposals, provide a brief description of Center successes and accomplishments based on the prior Phase of operation, with specific focus on research outcomes (i.e., innovations that have transitioned to industrial practice), educational outcomes (students placed in industrial positions or conducting industrially-relevant research as faculty members), academic outcomes (postdoctoral fellows, staff, and faculty who have earned recognition for quality research), and the financial and membership health of the Center during the prior NSF funded Phase.
Similarly, for Phase I proposals, provide outcomes from the Planning Grant process.
The remaining 10 to 15 pages of the “Site-Specific Content” should be unique to each Partner Site and include:
- Research Projects:
- Planning Grant proposals: List up to 5 prospective research projects per Site to be proposed to prospective IAB Members at the Center Planning Workshop.
- Phases I, II, II+, III: Discuss the envisioned research projects and each Site’s role, including: 1) breakthrough potential, innovative concepts, and value propositions; 2) the degree of collaboration and interdisciplinarity (cross-departmental, school and institution); 3) the broader societal and commercial impact of the research; and 4) any unique capabilities and contributions of the Site.
- Site addition: Describe specific projects to be undertaken at the Site and explain how this augments the Center’s research roadmap and existing capabilities.
- Workforce Development Plan. Discuss how the specific Site will contribute to training, internships and mentoring students of all levels, preparing them for future career paths to enhance the national workforce.
The PAPPG requirement to include Results from Prior NSF Support in the Project Description is waived. This information is now provided as Supplementary Document H.
C. Budget and Budget Justification
Planning Grants: Funds may be used for travel by Center/Site team members (e.g., post-docs, students, other essential personnel) to the Boot Camp and Planning Workshop, payment for the planning meeting room and/or AV rental, preparation of meeting materials, Center communications, consultants to create value from the planning activities, visits and engagement with prospective Member organizations and attendance, and faculty time. NSF funds may not be used for IAB travel or expenses.
Phases, I, II, II+, III, and Site Additions: NSF funds must be used toward management and operations of the IUCRC, such as: faculty time, Industry Liaison Officer time, event and travel costs of IAB meetings, Center communications, publications of Center research, and travel related to Member recruitment. Advance approval by the cognizant Program Director is required to use NSF funds for research. In multi-Site Centers, administrative and operational costs should be addressed as follows:
Budget Allocations for Center Operations and Management:
NSF funding for a university Site is intended to support operations, management, and administration at both the Center and Site levels. Site budgets must allocate NSF funds to the Lead Site for Center operations through one of two recommended approaches:
- Unequal NSF budgets: For a given NSF total Center budget, Partner Sites may consider requesting a smaller NSF budget request than the allowed maximum, permitting the Lead Site to request a larger NSF budget amount to cover the Center operation, management, and administrative costs.
- For an N-Site Center, the total annual Center budget for Phase I will be $150,000 x N; for Phase II it will be $100,000 x N; and for Phase II+ it will be $150,000 x N.
- Equal NSF budgets: All Sites may request the same allowed maximum NSF budget, but the Partner Sites are expected to budget for transfer of Center operations funds to the Lead Site through subawards. Prior to submission of the IUCRC proposals, the university Sites should execute and submit an MOU that establishes agreed upon indirect cost rates and processes for managing such transfers.
As part of the of the Center Description, the proposals must clearly specify the financial plan to contribute towards covering the costs of Center operations at the Lead Site.
D. Supplementary Documents
Include these required documents in the "Other Supplementary Documents" section of Research.gov (ForGrants.gov users, supplementary documents should be attached in Field 12 of the R&R Other Attachments.). Principal Investigators should refer to Table 3.
Note: Single-site Centers need to submit all supplementary documents listed in Table 3, with the sole exceptions of Supplementary Document D (Memorandum of Understanding) and I (Joint Letter of Support).
|
Supplementary Document |
Description |
Page limit |
Phases requiring this document |
Site in a multi-site center that must submit this document |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
A |
Letters of Interest |
2 pages per letter |
Planning Grant |
Lead Site Only (Lead Site supplies these for Site addition proposals) |
|
B |
Letters of Financial Commitment |
2 pages per letter |
Phases I, II, II+, III, Site Addition |
Lead Site Only (Lead Site supplies these for Site addition proposals) |
|
C |
Membership Certification |
N/A |
All Phase II, II+, III, and Site Addition |
Lead Site Only for Phase II, II+, and III (Lead Site supplies these for Site addition proposals) |
|
D |
Memorandum of Understanding |
N/A |
Phases I, II, II+, III, Site Addition |
Lead Site Only (Lead Site supplies these for Site addition proposals) |
|
E |
Documentation of Center Uniqueness Among IUCRCs |
2 pages |
Planning Grant and Phase I |
Lead Site Only |
|
F |
Data Management and Sharing Plan |
2 pages |
All |
Lead and Partner Sites |
|
G |
Mentoring Plan |
1 page |
All (if appropriate) |
Lead and Partner Sites |
|
H |
Results from Prior NSF Support |
1 page |
All |
Lead and Partner Sites |
|
I |
Joint Letter of Support |
2 pages per letter |
Site Addition |
Site seeking addition |
Explanation of Supplementary Documents:
A. Letters of Interest (Only for Planning Grants and only included in the Lead Site Proposal). For Site Addition, Lead Site/Center Director provides the letters to be included with the proposal.
Because a Center in the planning stage does not yet have committed Members, this supplementary document consists of Letters of Interest from a minimum of nine (9) potential Members times the number of Sites in a multi-Site Center (e.g., a 3-Site Center would need a minimum of 27 letters). A single-Site Center needs at least 24 Letters of Interest. In a Letter of Interest, an interested party should state how and why the organization may support the Center's concept and proposed research agenda, as well as the importance of the proposed Center to the interested party.
B. Letters of Financial Commitment (For Phase I, II, II+, III, and Site Addition; only included in the Lead Site Proposal). For Site Addition, Lead Site/Center Director provides the letters to be included with the proposal.
This package comprises the proposed initial IAB, with information on each Member’s eligibility and membership fee contribution. Each proposed Member must provide a letter with the following language:
Should {Center Name} be selected by NSF for funding, {Company Name} commits to joining {Center Name} as a {Full/ Associate} Member at the membership level of ${amount} on an annual basis, pending availability of funds, and accepting the NSF’s required Membership Agreement.
C. Membership Certification (For Phase II, II+, III, and Site Addition). For Site Addition, Lead Site/Center Director provides the certificate(s) to be included with the proposal.
For Phase II, II+, and III proposals, the Lead Site must include all the relevant prior phase official membership certifications, signed by the Authorized Organizational Representative (AOR) of the Sponsored Research Office (SRO) of the Center Lead or Partner Sites. For example, if the Center’s prior Phase I operated under a centralized funds collection model, the Lead Site of the Phase II proposal should attach the Phase I Center’s membership certification. On the other hand, if the prior Phase I Center operated under a Site based funds collection model, the Lead Site’s Phase II proposal should present all prior official membership certificates from Partner Sites, add the prior Lead Site membership certification, and include the package as Supplementary Document C in the proposal. This provides evidence of the eligible membership fee contributions and number of eligible distinct Members for the Center’s prior phase. This information will be used to verify that the Center’s prior Phase has met or exceeded IUCRC membership requirements.
For Site Addition proposals, the PI must work with the existing Center Director to collect and include as Supplementary Document C, all the existing Center’s pertinent official membership certification(s). This provides evidence of the eligible Membership Fee contributions and number of eligible distinct Members of the existing Center. This information, combined with the new financial commitments of prospective Members will be used to verify that the Center will still meet IUCRC requirements if the new Site is added.
D. Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) among Center's Sites (Common to all Sites; Phases I, II, II+, III, Site Addition). Only included in the Lead Site Proposal. For Site Addition, Lead Site/Center Director provides the MOU to be included in the Site addition proposal.
Describe how Sites plan to operate the Center, share administrative and managerial responsibilities, handle the collection and certification of membership fees, and the funding allocation based on Center’s selected research projects, The MOU(s) must be signed. For a Site Addition, the MOU must be executed.
E. Documentation of Center Uniqueness Among IUCRCs (Planning Grants and Phase I)
This justification is required for proposals where NSF has expressed concern about possible overlap in its response to the preliminary proposal. This letter is authored by the Center Director of an existing IUCRC if NSF has indicated concern about overlap. New IUCRCs must demonstrate limited to no overlap in research foci with an existing IUCRC.
F. Data Management and Sharing Plan (Center-wide and per Site as applicable)
Follow instructions in the PAPPG.
G. Mentoring Plan (Site-specific)
Follow instructions in the PAPPG.
H. Results from Prior NSF Support (Site-specific)
This document is required for all full proposals, but the content varies with proposal stage, as follows. Each Site must submit its own Results from Prior NSF Support for its own Site PIs.
Planning Grant– Discuss work conducted with prior or current NSF funding, focusing on the research area of interest to the Center or synergistic education and training activities.
Phase I – Describe the involvement of potential IAB Members in the Planning Workshop, the project selection process, the resulting proposed research projects, and the specific role of each Site. If NSF waived the Planning Grant requirement, describe Center planning events, workshops, and activities actively engaging industry and how that process aligned Center objectives with prospective Member needs. Discuss how research projects were selected.
Phase II, II+ or III – Describe the outcomes and impacts of Center research and membership growth. Each Site should discuss its specific role in the Center’s activities and successes.
I. Joint Letter of Support from the Director and IAB Chair of the Existing Center (Site Addition only)
This letter should clearly articulate the value of the new Site to the existing Center, describing the Center’s vetting.
B. Budgetary Information
Cost Sharing:
Inclusion of voluntary committed cost sharing is prohibited.
Indirect Cost (F&A) Limitations:
Membership fees received by the Center are considered program income. At least 90% of the IUCRC program income must be used to support direct costs of the research, and up to 10% may be used to support indirect costs.
NSF award funds are subject to an institution’s federally-negotiated indirect cost rate. See Special Award Conditions.
Other Budgetary Limitations:
Please refer to solicitation text.
Budget Preparation Instructions:
Please refer to solicitation text.
C. Due Dates
-
Preliminary Proposal Due Date(s) (required) (due by 5 p.m. submitting organization’s local time):
July 07, 2020
September 16, 2020
March 10, 2021
Second Wednesday in March, Annually Thereafter
September 08, 2021
Second Wednesday in September, Annually Thereafter
Preliminary proposals are required prior to submission of planning grants. Submitters seeking a waiver of the planning grant stage must submit the waiver request as a preliminary proposal.
-
Full Proposal Target Date(s):
September 08, 2020
December 16, 2020
June 09, 2021
Second Wednesday in June, Annually Thereafter
December 08, 2021
Second Wednesday in December, Annually Thereafter
D. Research.gov/Grants.gov Requirements
For Proposals Submitted Via Research.gov:
To prepare and submit a proposal via Research.gov, see detailed technical instructions available at: https://www.research.gov/research-portal/appmanager/base/desktop?_nfpb=true&_pageLabel=research_node_display&_nodePath=/researchGov/Service/Desktop/ProposalPreparationandSubmission.html. For Research.gov user support, call the Research.gov Help Desk at 1-800-673-6188 or e-mail rgov@nsf.gov. The Research.gov Help Desk answers general technical questions related to the use of the Research.gov system. Specific questions related to this program solicitation should be referred to the NSF program staff contact(s) listed in Section VIII of this funding opportunity.
For Proposals Submitted Via Grants.gov:
Before using Grants.gov for the first time, each organization must register to create an institutional profile. Once registered, the applicant's organization can then apply for any federal grant on the Grants.gov website. Comprehensive information about using Grants.gov is available on the Grants.gov Applicant Resources webpage: https://www.grants.gov/web/grants/applicants.html. In addition, the NSF Grants.gov Application Guide (see link in Section V.A) provides instructions regarding the technical preparation of proposals via Grants.gov. For Grants.gov user support, contact the Grants.gov Contact Center at 1-800-518-4726 or by email: support@grants.gov. The Grants.gov Contact Center answers general technical questions related to the use of Grants.gov. Specific questions related to this program solicitation should be referred to the NSF program staff contact(s) listed in Section VIII of this solicitation.
Submitting the Proposal: Once all documents have been completed, the Authorized Organizational Representative (AOR) must submit the application to Grants.gov and verify the desired funding opportunity and agency to which the application is submitted. The AOR must then sign and submit the application to Grants.gov. The completed application will be transferred to the Research.gov for further processing.
Proposers that submitted via Research.gov may use Research.gov to verify the status of their submission to NSF. For proposers that submitted via Grants.gov, until an application has been received and validated by NSF, the Authorized Organizational Representative may check the status of an application on Grants.gov. After proposers have received an e-mail notification from NSF, Research.gov should be used to check the status of an application.
VI. NSF Proposal Processing And Review Procedures
Proposals received by NSF are assigned to the appropriate NSF program for acknowledgement and, if they meet NSF requirements, for review. All proposals are carefully reviewed by a scientist, engineer, or educator serving as an NSF Program Officer, and usually by three to ten other persons outside NSF either as ad hoc reviewers, panelists, or both, who are experts in the particular fields represented by the proposal. These reviewers are selected by Program Officers charged with oversight of the review process. Proposers are invited to suggest names of persons they believe are especially well qualified to review the proposal and/or persons they would prefer not review the proposal. These suggestions may serve as one source in the reviewer selection process at the Program Officer's discretion. Submission of such names, however, is optional. Care is taken to ensure that reviewers have no conflicts of interest with the proposal. In addition, Program Officers may obtain comments from site visits before recommending final action on proposals. Senior NSF staff further review recommendations for awards. A flowchart that depicts the entire NSF proposal and award process (and associated timeline) is included in PAPPG Exhibit III-1.
A comprehensive description of the Foundation's merit review process is available on the NSF website at: https://www.nsf.gov/bfa/dias/policy/merit_review/.
Proposers should also be aware of core strategies that are essential to the fulfillment of NSF's mission, as articulated in Leading the World in Discovery and Innovation, STEM Talent Development and the Delivery of Benefits from Research - NSF Strategic Plan for Fiscal Years (FY) 2022 - 2026. These strategies are integrated in the program planning and implementation process, of which proposal review is one part. NSF's mission is particularly well-implemented through the integration of research and education and broadening participation in NSF programs, projects, and activities.
One of the strategic objectives in support of NSF's mission is to foster integration of research and education through the programs, projects, and activities it supports at academic and research institutions. These institutions must recruit, train, and prepare a diverse STEM workforce to advance the frontiers of science and participate in the U.S. technology-based economy. NSF's contribution to the national innovation ecosystem is to provide cutting-edge research under the guidance of the Nation's most creative scientists and engineers. NSF also supports development of a strong science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) workforce by investing in building the knowledge that informs improvements in STEM teaching and learning.
NSF's mission calls for the broadening of opportunities and expanding participation of groups, institutions, and geographic regions that are underrepresented in STEM disciplines, which is essential to the health and vitality of science and engineering. NSF is committed to this principle of diversity and deems it central to the programs, projects, and activities it considers and supports.
A. Merit Review Principles and Criteria
The National Science Foundation strives to invest in a robust and diverse portfolio of projects that creates new knowledge and enables breakthroughs in understanding across all areas of science and engineering research and education. To identify which projects to support, NSF relies on a merit review process that incorporates consideration of both the technical aspects of a proposed project and its potential to contribute more broadly to advancing NSF's mission "to promote the progress of science; to advance the national health, prosperity, and welfare; to secure the national defense; and for other purposes." NSF makes every effort to conduct a fair, competitive, transparent merit review process for the selection of projects.
1. Merit Review Principles
These principles are to be given due diligence by PIs and organizations when preparing proposals and managing projects, by reviewers when reading and evaluating proposals, and by NSF program staff when determining whether or not to recommend proposals for funding and while overseeing awards. Given that NSF is the primary federal agency charged with nurturing and supporting excellence in basic research and education, the following three principles apply:
- All NSF projects should be of the highest quality and have the potential to advance, if not transform, the frontiers of knowledge.
- NSF projects, in the aggregate, should contribute more broadly to achieving societal goals. These "Broader Impacts" may be accomplished through the research itself, through activities that are directly related to specific research projects, or through activities that are supported by, but are complementary to, the project. The project activities may be based on previously established and/or innovative methods and approaches, but in either case must be well justified.
- Meaningful assessment and evaluation of NSF funded projects should be based on appropriate metrics, keeping in mind the likely correlation between the effect of broader impacts and the resources provided to implement projects. If the size of the activity is limited, evaluation of that activity in isolation is not likely to be meaningful. Thus, assessing the effectiveness of these activities may best be done at a higher, more aggregated, level than the individual project.
With respect to the third principle, even if assessment of Broader Impacts outcomes for particular projects is done at an aggregated level, PIs are expected to be accountable for carrying out the activities described in the funded project. Thus, individual projects should include clearly stated goals, specific descriptions of the activities that the PI intends to do, and a plan in place to document the outputs of those activities.
These three merit review principles provide the basis for the merit review criteria, as well as a context within which the users of the criteria can better understand their intent.
2. Merit Review Criteria
All NSF proposals are evaluated through use of the two National Science Board approved merit review criteria. In some instances, however, NSF will employ additional criteria as required to highlight the specific objectives of certain programs and activities.
The two merit review criteria are listed below. Both criteria are to be given full consideration during the review and decision-making processes; each criterion is necessary but neither, by itself, is sufficient. Therefore, proposers must fully address both criteria. (PAPPG Chapter II.D.2.d(i). contains additional information for use by proposers in development of the Project Description section of the proposal). Reviewers are strongly encouraged to review the criteria, including PAPPG Chapter II.D.2.d(i), prior to the review of a proposal.
When evaluating NSF proposals, reviewers will be asked to consider what the proposers want to do, why they want to do it, how they plan to do it, how they will know if they succeed, and what benefits could accrue if the project is successful. These issues apply both to the technical aspects of the proposal and the way in which the project may make broader contributions. To that end, reviewers will be asked to evaluate all proposals against two criteria:
- Intellectual Merit: The Intellectual Merit criterion encompasses the potential to advance knowledge; and
- Broader Impacts: The Broader Impacts criterion encompasses the potential to benefit society and contribute to the achievement of specific, desired societal outcomes.
The following elements should be considered in the review for both criteria:
- What is the potential for the proposed activity to
- Advance knowledge and understanding within its own field or across different fields (Intellectual Merit); and
- Benefit society or advance desired societal outcomes (Broader Impacts)?
- To what extent do the proposed activities suggest and explore creative, original, or potentially transformative concepts?
- Is the plan for carrying out the proposed activities well-reasoned, well-organized, and based on a sound rationale? Does the plan incorporate a mechanism to assess success?
- How well qualified is the individual, team, or organization to conduct the proposed activities?
- Are there adequate resources available to the PI (either at the home organization or through collaborations) to carry out the proposed activities?
Broader impacts may be accomplished through the research itself, through the activities that are directly related to specific research projects, or through activities that are supported by, but are complementary to, the project. NSF values the advancement of scientific knowledge and activities that contribute to achievement of societally relevant outcomes. Such outcomes include, but are not limited to: full participation of women, persons with disabilities, and other underrepresented groups in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM); improved STEM education and educator development at any level; increased public scientific literacy and public engagement with science and technology; improved well-being of individuals in society; development of a diverse, globally competitive STEM workforce; increased partnerships between academia, industry, and others; improved national security; increased economic competitiveness of the United States; and enhanced infrastructure for research and education.
Proposers are reminded that reviewers will also be asked to review the Data Management and Sharing Plan and the Mentoring Plan, as appropriate.
Additional Solicitation Specific Review Criteria
Preliminary Proposals
IUCRC Center/Site Planning preliminary proposals are evaluated by NSF Program Officers and encouraged or discouraged based on the following:
- The critical importance, uniqueness, and innovation of the research area and its potential national economic impact.
- The size of the industry commitment supporting the Center.
- The quality and inter-institutional participation in Center-proposed research projects.
- Site team readiness and plan for recruiting new industry Members and retaining existing ones.
- Understanding of the goals of the IUCRC program and an appropriate implementation plan.
- Demonstrated independence of the proposed topic from existing IUCRCs.
- Approach to engaging a diverse mix of industry Members, including companies (large and small), startups, non-profit organizations, government agencies, and/or other interested non-academic entities.
Full IUCRC Proposals
Full proposals are subject to the following additional review criteria:
For Planning, Phase I, Phase II, Phase II+, and Phase III proposals:
- The potential for economic and societal impact;
- The degree to which the industry membership and commitments to participate in the proposed IUCRC has been met or exceeded;
- The degree to which unmet or underserved industrial needs may be addressed by cutting-edge, transformational pre-competitive research and the strength of potential industrial interest;
- The robustness of the plan to engage students from groups traditionally underrepresented in STEM disciplines, and to support and mentor underrepresented faculty, staff, and students;
- The commitment from faculty and the research infrastructure availability to maintain a viable Center that attracts and retains industry Members, and faculty success in Center-related research;
- The effectiveness of the plans for synergistic integration and collaborative efforts of all Sites in Center activities; and
- The effectiveness of the planned Center and Sites outreach activities in communicating with the public and Center stakeholders, as well as industry.
Additionally, for Phase II, Phase II+, and Phase III proposals:
- The extent to which knowledge/technology transfer to Members occurs, the generation of new Intellectual Property (IP) from Center activities, and the plan to both spin out new companies and support other new ventures in the sector of interest;
- The degree of participation and contribution of Center stakeholders (i.e., IAB Members, faculty, students, etc.) at the IAB meetings that occur twice a year;
- The number and quality of opportunities offered to students and postdocs to work closely with industry mentors and IAB companies, and the placement of students in IAB organizations or other companies in the sector;
- The quality and significance of the research outcomes and scientific accomplishments during the prior Phase; and
- The degree to which the Center met and exceeded the IUCRC financial and membership requirements during the prior Phase.
B. Review and Selection Process
Proposals submitted in response to this program solicitation will be reviewed by Ad hoc Review and/or Panel Review.
Reviewers will be asked to evaluate proposals using two National Science Board approved merit review criteria and, if applicable, additional program specific criteria. A summary rating and accompanying narrative will generally be completed and submitted by each reviewer and/or panel. The Program Officer assigned to manage the proposal's review will consider the advice of reviewers and will formulate a recommendation.
After scientific, technical and programmatic review and consideration of appropriate factors, the NSF Program Officer recommends to the cognizant Division Director whether the proposal should be declined or recommended for award. NSF strives to be able to tell applicants whether their proposals have been declined or recommended for funding within six months. Large or particularly complex proposals or proposals from new awardees may require additional review and processing time. The time interval begins on the deadline or target date, or receipt date, whichever is later. The interval ends when the Division Director acts upon the Program Officer's recommendation.
After programmatic approval has been obtained, the proposals recommended for funding will be forwarded to the Division of Grants and Agreements or the Division of Acquisition and Cooperative Support for review of business, financial, and policy implications. After an administrative review has occurred, Grants and Agreements Officers perform the processing and issuance of a grant or other agreement. Proposers are cautioned that only a Grants and Agreements Officer may make commitments, obligations or awards on behalf of NSF or authorize the expenditure of funds. No commitment on the part of NSF should be inferred from technical or budgetary discussions with a NSF Program Officer. A Principal Investigator or organization that makes financial or personnel commitments in the absence of a grant or cooperative agreement signed by the NSF Grants and Agreements Officer does so at their own risk.
Once an award or declination decision has been made, Principal Investigators are provided feedback about their proposals. In all cases, reviews are treated as confidential documents. Verbatim copies of reviews, excluding the names of the reviewers or any reviewer-identifying information, are sent to the Principal Investigator/Project Director by the Program Officer. In addition, the proposer will receive an explanation of the decision to award or decline funding.
VII. Award Administration Information
A. Notification of the Award
Notification of the award is made to the submitting organization by an NSF Grants and Agreements Officer. Organizations whose proposals are declined will be advised as promptly as possible by the cognizant NSF Program administering the program. Verbatim copies of reviews, not including the identity of the reviewer, will be provided automatically to the Principal Investigator. (See Section VI.B. for additional information on the review process.)
B. Award Conditions
An NSF award consists of: (1) the award notice, which includes any special provisions applicable to the award and any numbered amendments thereto; (2) the budget, which indicates the amounts, by categories of expense, on which NSF has based its support (or otherwise communicates any specific approvals or disapprovals of proposed expenditures); (3) the proposal referenced in the award notice; (4) the applicable award conditions, such as Grant General Conditions (GC-1)*; or Research Terms and Conditions* and (5) any announcement or other NSF issuance that may be incorporated by reference in the award notice. Cooperative agreements also are administered in accordance with NSF Cooperative Agreement Financial and Administrative Terms and Conditions (CA-FATC) and the applicable Programmatic Terms and Conditions. NSF awards are electronically signed by an NSF Grants and Agreements Officer and transmitted electronically to the organization via e-mail.
*These documents may be accessed electronically on NSF's Website at https://www.nsf.gov/awards/managing/award_conditions.jsp?org=NSF. Paper copies may be obtained from the NSF Publications Clearinghouse, telephone (703) 292-8134 or by e-mail from nsfpubs@nsf.gov.
More comprehensive information on NSF Award Conditions and other important information on the administration of NSF awards is contained in the NSF Proposal & Award Policies & Procedures Guide (PAPPG) Chapter VII, available electronically on the NSF Website at https://www.nsf.gov/publications/pub_summ.jsp?ods_key=pappg.
Administrative and National Policy Requirements
Build America, Buy America
As expressed in Executive Order 14005, Ensuring the Future is Made in All of America by All of America’s Workers (86 FR 7475), it is the policy of the executive branch to use terms and conditions of Federal financial assistance awards to maximize, consistent with law, the use of goods, products, and materials produced in, and services offered in, the United States.
Consistent with the requirements of the Build America, Buy America Act (Pub. L. 117-58, Division G, Title IX, Subtitle A, November 15, 2021), no funding made available through this funding opportunity may be obligated for an award unless all iron, steel, manufactured products, and construction materials used in the project are produced in the United States. For additional information, visit NSF’s Build America, Buy America webpage.
Special Award Conditions:
For the purpose of the IUCRC Program, NSF hereby clarifies that "project" is defined as a Center research activity. Each Site must demonstrate in its annual report how NSF funds and Program Income have furthered Center goals and objectives. It must also detail the amount and use of Center funds for the Site’s own administration and operations, for general Center administrative activities, and for conducting IAB-approved research projects at that Site.
Membership Fees and other funds received by the Center from Members of its IAB are considered Program Income (https://www.nsf.gov/pubs/policydocs/pappg22_1/pappg_8.jsp#VIIID4):
- Program Income should be used for IAB-recommended research projects and associated costs. At least 90 percent of the IUCRC program income must be used to support direct costs of the research, and up to 10 percent may be used to support indirect costs. The Center’s IAB may vote on the allocation of Program Income to support Center administrative or non-research related costs with cognizant Program Director approval.
- For the IUCRC program, Program Income need not be expended prior to the use of federal funds. However, no unexpended Program Income may remain at the end of the award. Unexpended funds must be remitted to NSF by crediting costs, otherwise chargeable against the grant. If it is not possible to record the credit via electronic system (ACM$), excess Program Income must be remitted to NSF electronically or by check, payable to the National Science Foundation.
- Center compliance with NSF requirements described in this solicitation (number of equivalent Full memberships and membership fee total) will be assessed annually. If a Center falls below the minimum membership requirements, it will be given a second year to comply in the next annual reporting period. If a Center continues to fall below minimum membership requirements for two consecutive years NSF may initiate appropriate corrective actions. This may include withholding future continuing grant increments for non-conforming Sites/Centers and/or adjusting the end date of their awards.
- If a Site is not contributing substantially on an annual basis to the Center, based on the number of projects and amount of Center funding it receives from working on IAB-related projects, NSF may initiate appropriate corrective actions. This may include withholding future continuing grant increments for underperforming Sites and/or adjusting the end date of their awards.
A Center seeking to transition from Phase I to the next phase will be expected to meet both the required number of equivalent Full memberships as well as Program Income from membership fee cash contributions on a cumulative basis over the duration of the Phase I award. For example, an N-Site IUCRC will be expected to present 5 years x ($150,000 x N) of Program Income from membership fees, and 5 years x (3 x N) equivalent full memberships summing across each year of the grant.
For instance, a N=2 Center with a Full membership level of $50,000/year has requirements of 6 Full memberships or equivalent as per Table 1. If it maintains equivalent Full memberships of 6, 5, 6, 6, 7 in Years 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 respectively, the cumulative equivalent Full memberships would be 30 and the cumulative membership fees would be $1,500,000, and thus this Center would meet the NSF requirement. However, if the Center maintained 6, 5, 6, 6, 6 equivalent Full memberships, it would fall short of the NSF requirement for both cumulative cash contributions as well as cumulative equivalent Full memberships and potentially be subject to corrective action.
- If a Lead Site is found to be underperforming, NSF may consult with the IAB and other Site Directors to explore the possibility of changing Center Directors and/or the Lead Site designation.
C. Reporting Requirements
For all multi-year grants (including both standard and continuing grants), the Principal Investigator must submit an annual project report to the cognizant Program Officer no later than 90 days prior to the end of the current budget period. (Some programs or awards require submission of more frequent project reports). No later than 120 days following expiration of a grant, the PI also is required to submit a final annual project report, and a project outcomes report for the general public.
Failure to provide the required annual or final annual project reports, or the project outcomes report, will delay NSF review and processing of any future funding increments as well as any pending proposals for all identified PIs and co-PIs on a given award. PIs should examine the formats of the required reports in advance to assure availability of required data.
PIs are required to use NSF's electronic project-reporting system, available through Research.gov, for preparation and submission of annual and final annual project reports. Such reports provide information on accomplishments, project participants (individual and organizational), publications, and other specific products and impacts of the project. Submission of the report via Research.gov constitutes certification by the PI that the contents of the report are accurate and complete. The project outcomes report also must be prepared and submitted using Research.gov. This report serves as a brief summary, prepared specifically for the public, of the nature and outcomes of the project. This report will be posted on the NSF website exactly as it is submitted by the PI.
More comprehensive information on NSF Reporting Requirements and other important information on the administration of NSF awards is contained in the NSF Proposal & Award Policies & Procedures Guide (PAPPG) Chapter VII, available electronically on the NSF Website at https://www.nsf.gov/publications/pub_summ.jsp?ods_key=pappg.
Additional Reporting Requirements:
IUCRC awards require additional reporting requirements. These requirements are currently undergoing the information collection review process and the clearance number will be included with the reporting requirements. For updated information, PIs are encouraged to consult the IUCRC website (https://iucrc.nsf.gov/) prior to submitting their annual reports.
VIII. Agency Contacts
Please note that the program contact information is current at the time of publishing. See program website for any updates to the points of contact.
General inquiries regarding this program should be made to:
-
Prakash G. Balan, IUCRC Lead Program Director, Directorate for Engineering, telephone: (703) 292-5341, email: pbalan@nsf.gov
Seetha Raghavan, IUCRC Program Director, telephone: (703) 292-4580, email: seraghav@nsf.gov
-
Mohan Kumar, IUCRC Program Director, Directorate for Computer & Information Science & Engineering, telephone: (703) 292-7408, email: mokumar@nsf.gov
-
Ann C. Von Lehmen, IUCRC Program Director, Directorate for Computer & Information Science & Engineering, telephone: (703) 292-4756, email: avonlehm@nsf.gov
-
Barbara L. Ransom, IUCRC Program Director, Directorate for Geosciences, telephone: (703) 292-7792, email: bransom@nsf.gov
-
Rebecca Ferrell, IUCRC Program Director, Directorate for Social, Behavioral & Economic Sciences, telephone: (703) 292-7850, email: rferrell@nsf.gov
Jeffrey M. Stanton, IUCRC Program Director, telephone: (703) 292-7794, email: jstanton@nsf.gov
Thomas S. Woodson, IUCRC Program Director, telephone: (703) 292-5150, email: tswoodso@nsf.gov
-
José R. Almirall, IUCRC Program Director, Directorate for Mathematical and Physical Sciences, telephone: (703) 292-7434, email: jalmiral@nsf.gov
For questions related to the use of NSF systems, contact:
- NSF Help Desk: 1-800-673-6188
- Research.gov Help Desk e-mail: rgov@nsf.gov
For questions relating to Grants.gov contact:
-
Grants.gov Contact Center: If the Authorized Organizational Representatives (AOR) has not received a confirmation message from Grants.gov within 48 hours of submission of application, please contact via telephone: 1-800-518-4726; e-mail: support@grants.gov.
Note: For Directorates with topic-specific portfolios (i.e., Geosciences; Social, Behavioral, and Economic Sciences), IUCRCs will be considered only on topics of interest distributed via Dear Colleague Letters. Please check the NSF website or call the cognizant Program Director for more information.
IX. Other Information
The NSF website provides the most comprehensive source of information on NSF Directorates (including contact information), programs and funding opportunities. Use of this website by potential proposers is strongly encouraged. In addition, "NSF Update" is an information-delivery system designed to keep potential proposers and other interested parties apprised of new NSF funding opportunities and publications, important changes in proposal and award policies and procedures, and upcoming NSF Grants Conferences. Subscribers are informed through e-mail or the user's Web browser each time new publications are issued that match their identified interests. "NSF Update" also is available on NSF's website.
Grants.gov provides an additional electronic capability to search for Federal government-wide grant opportunities. NSF funding opportunities may be accessed via this mechanism. Further information on Grants.gov may be obtained at https://www.grants.gov.
About The National Science Foundation
The National Science Foundation (NSF) is an independent Federal agency created by the National Science Foundation Act of 1950, as amended (42 USC 1861-75). The Act states the purpose of the NSF is "to promote the progress of science; [and] to advance the national health, prosperity, and welfare by supporting research and education in all fields of science and engineering."
NSF funds research and education in most fields of science and engineering. It does this through grants and cooperative agreements to more than 2,000 colleges, universities, K-12 school systems, businesses, informal science organizations and other research organizations throughout the US. The Foundation accounts for about one-fourth of Federal support to academic institutions for basic research.
NSF receives approximately 55,000 proposals each year for research, education and training projects, of which approximately 11,000 are funded. In addition, the Foundation receives several thousand applications for graduate and postdoctoral fellowships. The agency operates no laboratories itself but does support National Research Centers, user facilities, certain oceanographic vessels and Arctic and Antarctic research stations. The Foundation also supports cooperative research between universities and industry, US participation in international scientific and engineering efforts, and educational activities at every academic level.
Facilitation Awards for Scientists and Engineers with Disabilities (FASED) provide funding for special assistance or equipment to enable persons with disabilities to work on NSF-supported projects. See the NSF Proposal & Award Policies & Procedures Guide Chapter II.F.7.6 for instructions regarding preparation of these types of proposals.
The National Science Foundation has Telephonic Device for the Deaf (TDD) and Federal Information Relay Service (FIRS) capabilities that enable individuals with hearing impairments to communicate with the Foundation about NSF programs, employment or general information. TDD may be accessed at (703) 292-5090 and (800) 281-8749, FIRS at (800) 877-8339.
The National Science Foundation Information Center may be reached at (703) 292-5111.
|
The National Science Foundation promotes and advances scientific progress in the United States by competitively awarding grants and cooperative agreements for research and education in the sciences, mathematics, and engineering. To get the latest information about program deadlines, to download copies of NSF publications, and to access abstracts of awards, visit the NSF Website at https://www.nsf.gov
|
Privacy Act And Public Burden Statements
The information requested on proposal forms and project reports is solicited under the authority of the National Science Foundation Act of 1950, as amended. The information on proposal forms will be used in connection with the selection of qualified proposals; and project reports submitted by awardees will be used for program evaluation and reporting within the Executive Branch and to Congress. The information requested may be disclosed to qualified reviewers and staff assistants as part of the proposal review process; to proposer institutions/grantees to provide or obtain data regarding the proposal review process, award decisions, or the administration of awards; to government contractors, experts, volunteers and researchers and educators as necessary to complete assigned work; to other government agencies or other entities needing information regarding applicants or nominees as part of a joint application review process, or in order to coordinate programs or policy; and to another Federal agency, court, or party in a court or Federal administrative proceeding if the government is a party. Information about Principal Investigators may be added to the Reviewer file and used to select potential candidates to serve as peer reviewers or advisory committee members. See System of Record Notices, NSF-50, "Principal Investigator/Proposal File and Associated Records," and NSF-51, "Reviewer/Proposal File and Associated Records.” Submission of the information is voluntary. Failure to provide full and complete information, however, may reduce the possibility of receiving an award.
An agency may not conduct or sponsor, and a person is not required to respond to, an information collection unless it displays a valid Office of Management and Budget (OMB) control number. The OMB control number for this collection is 3145-0058. Public reporting burden for this collection of information is estimated to average 120 hours per response, including the time for reviewing instructions. Send comments regarding the burden estimate and any other aspect of this collection of information, including suggestions for reducing this burden, to:
Suzanne H. Plimpton
Reports Clearance Officer
Policy Office, Division of Institution and Award Support
Office of Budget, Finance, and Award Management
National Science Foundation
Alexandria, VA 22314


Please refer to NSF 20-080 for Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) related to this program solicitation.